



Next: 3.3.3 Raymond-thermal spectrum example
Up: 3.3 Expected Count Rates
Previous: 3.3.1 Blackbody spectrum example
3.3.2 Power-law spectrum example
Consider a distant AGN with a power law spectrum of energy slope 0.5
which is at a luminosity distance of 1000 Mpc and is viewed through an
absorption column of 5 x 1020 cm-2 (log(N
H) = 20.7).
The AGN luminosity in the ROSAT band is Lx = 1044 ergs s-1.
We want to determine how long an observation is required for a
10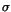 detection. The unabsorbed flux is
FS, 0 = 8.37 x 10-13 ergs cm-2 s-1.
The ECF for this spectral model is
taken from Table 8 or Figure 30, it is
1.75 x 1010,
which gives a count rate 0.0146 ct s-1. Using the
sensitivity formula from Section 3.2.1 with R=0.0073 ct s-1 (50% of
the total so as to refer to
the 5
'' x 5'' detect cell), we calculate that the
observation time needed to detect this source at the 10
detection. The unabsorbed flux is
FS, 0 = 8.37 x 10-13 ergs cm-2 s-1.
The ECF for this spectral model is
taken from Table 8 or Figure 30, it is
1.75 x 1010,
which gives a count rate 0.0146 ct s-1. Using the
sensitivity formula from Section 3.2.1 with R=0.0073 ct s-1 (50% of
the total so as to refer to
the 5
'' x 5'' detect cell), we calculate that the
observation time needed to detect this source at the 10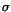 level
is about 13,700 seconds.
level
is about 13,700 seconds.
rsdc@cfa.harvard.edu
1999-05-25